Hub def takes center stage as we delve into the multifaceted world of central points and places. From transportation hubs that connect cities to social hubs that foster community, hubs play a pivotal role in shaping our society and infrastructure.
Hubs serve as meeting points, facilitating the flow of people, ideas, and resources. They are the crossroads where connections are forged, and accessibility is enhanced. Whether it’s a bustling airport, a vibrant marketplace, or a thriving digital platform, hubs are the catalysts that drive progress and innovation.
Definition of Hub: Hub Def

A hub is a central point or place from which other things diverge or converge. It serves as a focal point or a place of convergence and distribution.
The term “hub” is commonly used in various contexts, such as:
- Transportation hubs:Airports, train stations, and bus terminals that connect different modes of transportation and facilitate travel.
- Communication hubs:Internet exchanges, data centers, and telecommunication centers that provide connectivity and data transmission.
- Social hubs:Community centers, libraries, and public spaces that foster social interactions and community engagement.
The word “hub” is derived from the Middle English word “hubbe,” meaning “a central point” or “a center.” It is believed to have originated from the Old English word “hob,” which referred to a raised area or a mound.
Types of Hubs
There are various types of hubs, each with its own characteristics and functions:
Transportation Hubs
- Airports:Airports serve as hubs for air travel, connecting cities and countries through scheduled flights.
- Train stations:Train stations are hubs for rail transportation, providing connectivity between cities and regions.
- Bus terminals:Bus terminals are hubs for bus transportation, offering services for intercity and regional travel.
Communication Hubs
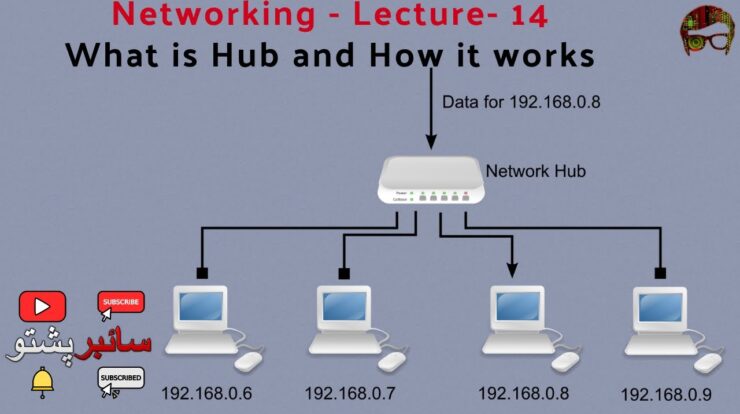
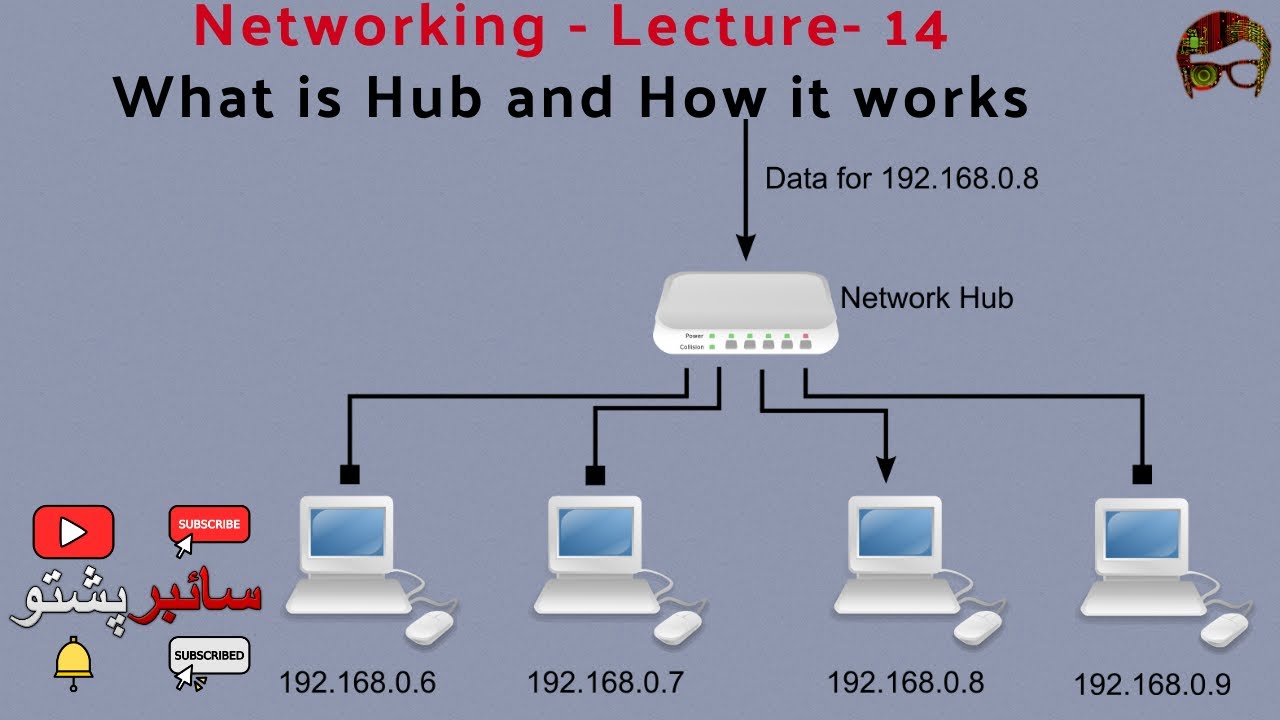
- Internet exchanges:Internet exchanges are hubs for internet traffic, facilitating the exchange of data between different networks.
- Data centers:Data centers are hubs for storing and processing large amounts of data, providing infrastructure for cloud computing and online services.
- Telecommunication centers:Telecommunication centers are hubs for telecommunication networks, providing services such as phone calls, data transmission, and internet connectivity.
Social Hubs
- Community centers:Community centers are hubs for social activities, offering programs and services for community members.
- Libraries:Libraries are hubs for knowledge and information, providing access to books, resources, and educational programs.
- Public spaces:Public spaces, such as parks and plazas, are hubs for social interactions and community gatherings.
Importance of Hubs
Hubs play a crucial role in society and infrastructure, offering numerous benefits:
- Economic benefits:Hubs facilitate trade, tourism, and investment by connecting people and businesses.
- Social benefits:Hubs foster social interactions, community building, and cultural exchange.
- Cultural benefits:Hubs preserve and promote cultural heritage, providing platforms for artistic expression and community events.
Furthermore, hubs enhance connectivity and accessibility:
- Connectivity:Hubs provide seamless connections between different transportation modes, communication networks, and social groups.
- Accessibility:Hubs make it easier for people to access services, resources, and opportunities, regardless of their location or background.
Hub Design and Planning, Hub def
Designing and planning hubs involves careful consideration of various factors:
- Location:Hubs should be strategically located to maximize accessibility and connectivity.
- Capacity:Hubs should have sufficient capacity to accommodate the anticipated volume of traffic or usage.
- Connectivity:Hubs should be designed to seamlessly integrate with other transportation systems, communication networks, or social services.
Innovative hub designs focus on optimizing efficiency and accessibility:
- Multi-modal hubs:Hubs that integrate multiple transportation modes, such as airports with train stations or bus terminals.
- Smart hubs:Hubs that utilize technology to improve efficiency, such as automated ticketing systems or real-time traffic monitoring.
- Sustainable hubs:Hubs that incorporate sustainable practices, such as energy-efficient lighting or green building materials.
Emerging Trends in Hub Development
Hub development is influenced by emerging trends and technologies:
- Advancements in transportation:High-speed rail, autonomous vehicles, and electric transportation are transforming hub design.
- Communication advancements:5G networks, fiber optics, and satellite technology are enhancing connectivity and data transmission.
- Smart technologies:Artificial intelligence, IoT, and cloud computing are enabling smart hubs with automated systems and data-driven decision-making.
Additionally, sustainability and resilience are becoming increasingly important in hub development:
- Sustainability:Hubs are incorporating renewable energy sources, green building materials, and waste reduction measures.
- Resilience:Hubs are being designed to withstand natural disasters and other disruptions, ensuring continuity of operations.
Outcome Summary
As technology continues to advance and the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the importance of hubs will only grow. By embracing innovative designs, leveraging emerging technologies, and prioritizing sustainability, we can create hubs that are not only efficient and accessible but also resilient and adaptable to the challenges of the future.
FAQ Corner
What is the primary meaning of “hub”?
A hub is a central point or place that serves as a connecting point or focal point for activity.
What are the different types of hubs?
Hubs can be categorized into various types, including transportation hubs, communication hubs, and social hubs, each with its unique characteristics and functions.
Why are hubs important?
Hubs play a crucial role in society and infrastructure, providing economic, social, and cultural benefits by enhancing connectivity and accessibility.